How to differentiate phone types
I have the following problem: the customer will send me a phone number and I need to differentiate whether it is fixed or mobile, does anyone know some rules that distinguish the two groups well?
7 answers
O Numbering Plan it is the mode of Organization of the numbers of telecommunications services of public use. The table below has the relationship between the landline and mobile number ranges, based on this I think it is easy to solve your problem.
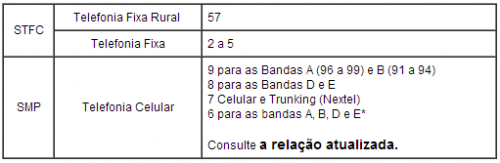
Source: Teleco
Structure of the Brazilian telephone system
Numbers can essentially have 4 portions:
-
Country prefix (two digits):
Country calling code: +55
-
Operator prefix (two digits):
12 - CTB
14 - Brasil Telecom
15 - Telefonica
21 - Sound
23 - Brasil
25 - COMPANY
31 - Hi
41 - TIM -
Geographical prefix (two digits): Wikipedia
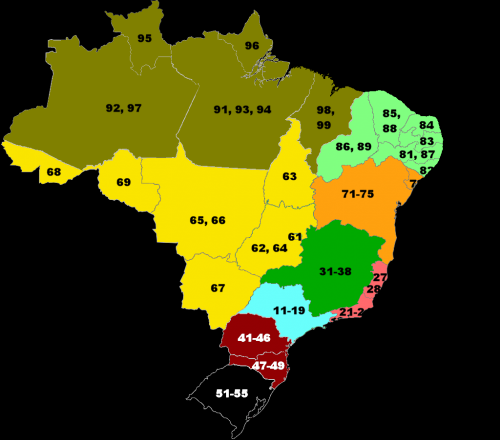
-
Phone number in formats:
NNNN-NNNN 9NNNN-NNNN
In addition, there are other numbers with a special nomenclature, the public utility numbers containing only 3 digits.
Types of numbers
There are only two types of numbers, fixed or movable, distinguished from each other by the first digit:
- 2 to 5 are fixed numbers (land line)
- 6 to 9 are mobile numbers (mobile phone)
Pseudocode
Based on the above data, the algorithm would have to work within the following templates:
-
Check if it has more than three digits to determine if it is a public utility number.
If for public use, we end here and act accordingly.
-
Check If number starts with
+55to determine if it has the country calling code.If you have the country calling code, we will remove it from the number and continue with the verification.
-
Check if it has at least 12 digits.
If it does not have 12 or more digits, it is invalid, we end here and act accordingly.
-
Check for 13 digits.
If you have 13 digit, It is mobile number of São Paulo, we end here and act accordingly.
-
Check whether fixed or movable.
Arriving here we have to have 12 digits, as such, we will take the 5th digit and check if the same is in the group (2~5) or in the Group (6~9), we finish the operation and act accordingly.
-
Optional:
Break the 12 digits into portions to identify where the same:
2 dígitos - Operadora 2 dígitos - Área geográfica 4 dígitos - Primeira parte do número 4 dígitos - Segunda parte do número
Diagram
The flow of information based on what we have determined so far can be presented as follows:
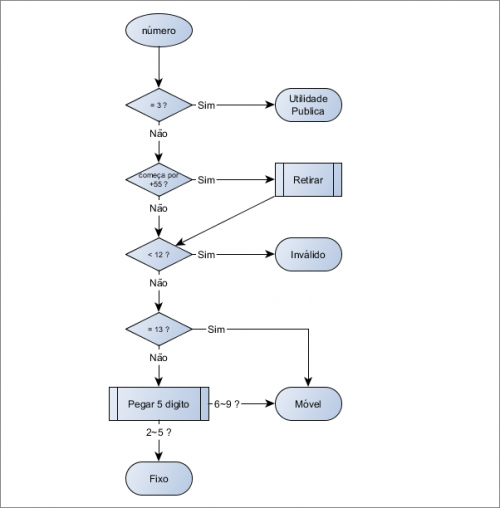
Code
Putting this whole exercise into practice, let's implement the solution with JavaScript:
document.getElementById("validar").onclick = function() {
var continuar = true,
numero = document.getElementById('numero').value;
// Verificar se vazio
if (numero.length === 0) {
alert("Brincalhão, preenche lá o número!");
continuar = false;
}
// Verificar se número é de utilidade publica
if (numero.length === 3) {
alert("Número de utilidade publica");
continuar = false;
}
// Verificar se tem código do país para retirar
if (continuar && numero.substring(0, 3) === "+55") {
numero = numero.substring(3);
}
// Verificar se menos que 12 digitos
if (continuar && numero.length < 12) {
alert("Número inválido, por favor introduza Cod. Operadora + Cod. Area + Numero");
continuar = false;
}
// Verificar se contém 13 digitos
if (continuar && numero.length === 13) {
alert("Número móvel");
continuar = false;
}
// Verificar se o 5º digito
var digitoControlo = numero.charAt(4);
if (continuar) {
if (digitoControlo >= 2 && digitoControlo <= 5) {
alert("Número fixo");
} else if (digitoControlo >= 6 && digitoControlo <= 9) {
alert("Número móvel");
} else {
alert("Número especial");
}
}
}<form>
<input type="text" id="numero" name="numero" />
<button id="validar">validar</button>
</form>Notes:
There are other checks to perform, such as if there are no letters in place of numbers, but such checks do not they are part of the clearance of the number and must be taken into account before it is started.
Some of the checks may not even be required, it goes from the implementation of each, reason why they are separate, becoming modular.
I am Portuguese from Portugal, if I missed any details about the structure of" your " telephone system, leave a comment, I will be happy to update the answer.
Currently by anatel only phone numbers that start with 6,7,8,9 are mobile numbers. you can do a regex to interpret this . Remembering that it is only the phone number not including ddd.
You can use Twillo's new lookup service.
With the paid module it gives you the type of number (mobile or fixed) and the operator too.
curl -X GET https://lookups.twilio.com/v1/PhoneNumbers/55-11-5525-6325\
-d "Type=carrier"
-u "{AccountSid}:{AuthToken}"
{
"country_code": "BR",
"phone_number": "+551155256325",
"national_format": "(11) 5525-6325",
"url": "https://lookups.twilio.com/v1/PhoneNumber/+551155256325",
"carrier": {
"type": "landline",
"error_code": null,
"mobile_network_code": null,
"mobile_country_code": null,
"name": "Vivo"
}
}
After studying the answer of Zuul and analyzing this article of Anatel, I adapted his solution (in JavaScript) for the two main programming languages I use: Java and Object Pascal. Creating the respective classes. And the code has been tested and is working for numbers with and without the ninth digit .
However, I made some changes, to accept special numbers, such as 0300, 0500, 0800, 0900, 3003, 4003 and 4004. Fix some bugs when the user enters the numbers with zeroes, for example: (OP) 041 (AREA) 87 (A) 9999-9999, or (OP) 41 (AREA) 087 (A) 9999-9999.
Below the class code.
In Java :
/*
Telefone - Retorna o tipo de um número de telefone (fixo, móvel, público etc.)
Baseado neste tópico:
. https://pt.stackoverflow.com/questions/14343/como-diferenciar-tipos-de-telefone
Autores:
. Silvio Clécio - github.com/silvioprog
*/
package br.com.duallsistemas.telefone;
/**
* Created by silvioprog on 06/04/2015.
*/
public class Telefone {
private String numero;
private String ddd;
private String codOperadora;
public Telefone(String codOperadora, String ddd, String numero) {
this.codOperadora = apenasNumeros(apenasString(codOperadora));
this.ddd = apenasNumeros(apenasString(ddd));
setNumero(numero);
}
public Telefone(String codOperadora, String ddd) {
this(codOperadora, ddd, "");
}
public Telefone() {
this("", "");
}
private boolean inRange(int num, int min, int max) {
return num >= min && num <= max;
}
private boolean numeroEspecial() {
return numero.startsWith("0300") || numero.startsWith("0500") || numero.startsWith("0800") ||
numero.startsWith("0900") || numero.startsWith("3003") || numero.startsWith("4003") ||
numero.startsWith("4004");
}
private boolean temNonoDigito() {
Integer i = Integer.parseInt(numero.substring(0, 2));
return inRange(i, 11, 19) || inRange(i, 21, 24) || i == 27 || i == 28 || inRange(i, 91, 99);
}
protected String apenasNumeros(String s) {
if (s == null)
return "";
String result = "";
for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
if (c >= '0' && c <= '9')
result += c;
}
return result;
}
protected String apenasString(String s) {
if (s == null)
return "";
s = s.trim();
if (s.equals(""))
return "";
return s;
}
public String getCodOperadora() {
return codOperadora;
}
public String getDdd() {
return ddd;
}
public TipoTelefone obtemTipo() {
int len = numero.length();
if (len <= 2)
return TipoTelefone.INVALIDO;
if (len == 3)
return TipoTelefone.PUBLICO;
if (len < 12) {
if (numeroEspecial())
return TipoTelefone.ESPECIAL;
else
return TipoTelefone.INVALIDO;
}
if (len == 13)
return TipoTelefone.MOVEL;
char digito;
if (len == 15)
digito = numero.charAt(7);
else
digito = numero.charAt(4);
if (digito >= '2' && digito <= '5')
return TipoTelefone.FIXO;
if (digito >= '6' && digito <= '9')
return TipoTelefone.MOVEL;
return TipoTelefone.ESPECIAL;
}
public String getDescricao() {
return String.valueOf(obtemTipo());
}
public String getNumero() {
return numero;
}
public void setNumero(String numero) {
numero = apenasString(numero);
if (numero.equals(""))
return;
if (numero.startsWith("+55"))
numero = numero.substring(3);
this.numero = apenasNumeros(numero);
int len = this.numero.length();
if (len == 8 ) {
if (!numeroEspecial())
this.numero = codOperadora + ddd + this.numero;
} else if (len == 9)
this.numero = codOperadora + ddd + this.numero;
else if (len == 10)
this.numero = codOperadora + this.numero;
else if (len == 11 || len == 14) {
if (!numeroEspecial() && this.numero.substring(0, 1).equals("0")) {
this.numero = this.numero.substring(1);
this.numero = codOperadora + this.numero;
} else if (temNonoDigito())
this.numero = codOperadora + this.numero;
}
}
}
Usage example (note: the numbers used in the example are fictitious):
package br.com.duallsistemas;
import br.com.duallsistemas.telefone.Telefone;
public class Main {
public static void imprime(Telefone tel, String numero) {
tel.setNumero(numero);
System.out.println("NUMERO REAL: " + tel.getNumero() + ", TIPO: " + tel.getDescricao());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Telefone tel = new Telefone("41", "65");
System.out.println("INTRODUZA O NUMERO DO SEGUINTE FORMATO: COD. OPERADORA + COD. AREA + NUMERO");
System.out.println("=======");
System.out.println();
// inválidos
imprime(tel, "12");
imprime(tel, "+55 41 (99) 999-9999");
System.out.println();
// público
imprime(tel, "190");
System.out.println();
// especial
imprime(tel, "0300 313 4701");
imprime(tel, "0500 313 4701");
imprime(tel, "0800 729 0722");
imprime(tel, "0900 313 4701");
imprime(tel, "3003 3030");
imprime(tel, "4003 3030");
imprime(tel, "4004 3030");
System.out.println();
// fixo
imprime(tel, "3549-5589");
imprime(tel, "(87) 3549-5589");
System.out.println();
// movel
imprime(tel, "9985-0997");
imprime(tel, "(87) 9985-0997");
imprime(tel, "31 (87) 9985-0997");
imprime(tel, "+55 31 (87) 9985-0997");
System.out.println();
// movel SP
imprime(tel, "9 9985-0997");
imprime(tel, "(11) 9 9985-0997");
imprime(tel, "31 (11) 9 9985-0997");
imprime(tel, "031 (11) 9 9985-0997");
}
}
In Object Pascal (compatible with free Pascal 2.6.4 + and Delphi 7+):
(*
TTelefone - Retorna o tipo de um número de telefone (fixo, móvel, público etc.)
Baseado neste tópico:
. https://pt.stackoverflow.com/questions/14343/como-diferenciar-tipos-de-telefone
Autores:
. Silvio Clécio - github.com/silvioprog
*)
unit Telefone;
{$IFDEF FPC}
{$mode objfpc}{$H+}
{$ENDIF}
interface
uses
SysUtils;
type
{ TTipoTelefone }
TTipoTelefone = (ttInvalido, ttPublico, ttFixo, ttMovel, ttEspecial);
{ TTelefone }
TTelefone = class(TObject)
private
FNumero: string;
FDdd: string;
FCodOperadora: string;
function GetCodOperadora: string;
function GetDdd: string;
function GetDescricao: string;
function GetTipo: TTipoTelefone;
procedure SetNumero(ANumero: string);
function TemNonoDigito: Boolean;
function NumeroEspecial: Boolean;
public
constructor Create(const ACodOperadora, ADdd, ANumero: string); overload; virtual;
constructor Create(const ACodOperadora, ADdd: string); overload; virtual;
constructor Create; overload; virtual;
function ApenasNumeros(const S: string): string;
function ApenasString(const S: string): string;
property CodOperadora: string read GetCodOperadora;
property Ddd: string read GetDdd;
property Numero: string read FNumero write SetNumero;
property Descricao: string read GetDescricao;
property Tipo: TTipoTelefone read GetTipo;
end;
const
DESC_TELEFONE: array[TTipoTelefone] of string = (
'INVALIDO', 'PUBLICO', 'FIXO', 'MOVEL', 'ESPECIAL'
);
implementation
{ TTelefone }
constructor TTelefone.Create(const ACodOperadora, ADdd, ANumero: string);
begin
inherited Create;
FCodOperadora := ApenasNumeros(ApenasString(ACodOperadora));
FDdd := ApenasNumeros(ApenasString(ADdd));
SetNumero(ANumero);
end;
constructor TTelefone.Create(const ACodOperadora, ADdd: string);
begin
Create(ACodOperadora, ADdd, '');
end;
constructor TTelefone.Create;
begin
Create('', '');
end;
function TTelefone.TemNonoDigito: Boolean;
var
I, E: Integer;
begin
Val(Copy(FNumero, 1, 2), I, E);
Result := E = 0;
if Result then
case I of
11..19, 21..24, 27, 28, 91..99: Result := True;
else
Result := False;
end;
end;
function TTelefone.NumeroEspecial: Boolean;
var
N: ShortString;
begin
N := Copy(FNumero, 1, 4);
Result := (N = '0300') or (N = '0500') or (N = '0800') or (N = '0900') or
(N = '3003') or (N = '4003') or (N = '4004');
end;
function TTelefone.ApenasNumeros(const S: string): string;
var
C: Char;
{$IFNDEF FPC}
I: Integer;
{$ENDIF}
begin
Result := '';
{$IFDEF FPC}
for C in S do
if (C >= '0') and (C <= '9') then
Result += C;
{$ELSE}
for I := 1 to Length(S) do
begin
C := S[I];
if (C >= '0') and (C <= '9') then
Result := Result + C;
end;
{$ENDIF}
end;
function TTelefone.ApenasString(const S: string): string;
begin
Result := Trim(S);
end;
function TTelefone.GetCodOperadora: string;
begin
Result := FCodOperadora;
end;
function TTelefone.GetDdd: string;
begin
Result := FDdd;
end;
function TTelefone.GetTipo: TTipoTelefone;
var
D: Byte;
L
{$IFNDEF FPC}
, E
{$ENDIF}
: Integer;
begin
L := Length(FNumero);
{$IFDEF FPC}
if L <= 2 then
Exit(ttInvalido);
if L = 3 then
Exit(ttPublico);
if L < 12 then
begin
if NumeroEspecial then
Exit(ttEspecial)
else
Exit(ttInvalido);
end;
if L = 13 then
Exit(ttMovel);
if L = 15 then
Val(FNumero[8], D)
else
Val(FNumero[5], D);
if (D >= 2) and (D <= 5) then
Exit(ttFixo);
if (D >= 6) and (D <= 9) then
Exit(ttMovel);
Result := ttEspecial;
{$ELSE}
if L <= 2 then
Result := ttInvalido
else if L = 3 then
Result := ttPublico
else if L < 12 then
begin
if NumeroEspecial then
Result := ttEspecial
else
Result := ttInvalido;
end
else if L = 13 then
Result := ttMovel
else
begin
if L = 15 then
Val(FNumero[8], D, E)
else
Val(FNumero[5], D, E);
if (D >= 2) and (D <= 5) then
Result := ttFixo
else if (D >= 6) and (D <= 9) then
Result := ttMovel
else
Result := ttEspecial;
end;
{$ENDIF}
end;
function TTelefone.GetDescricao: string;
begin
Result := DESC_TELEFONE[GetTipo];
end;
procedure TTelefone.SetNumero(ANumero: string);
var
L: Integer;
begin
ANumero := ApenasString(ANumero);
if ANumero = '' then
Exit;
if Copy(ANumero, 1, 3) = '+55' then
ANumero := Copy(ANumero, 4, MaxInt);
FNumero := ApenasNumeros(ANumero);
L := Length(FNumero);
if L = 8 then
begin
if not NumeroEspecial then
FNumero := FCodOperadora + FDdd + FNumero;
end else if L = 9 then
FNumero := FCodOperadora + FDdd + FNumero
else if L = 10 then
FNumero := FCodOperadora + FNumero
else if (L = 11) or (L = 14) then
if (not NumeroEspecial) and (Copy(FNumero, 1, 1) = '0') then
begin
Delete(FNumero, 1, 1);
FNumero := FCodOperadora + FNumero;
end
else if TemNonoDigito then
FNumero := FCodOperadora + FNumero;
end;
end.
Example of use:
program test;
{$IFDEF FPC}
{$mode objfpc}{$H+}
{$ENDIF}
uses
Telefone;
procedure imprime(tel: TTelefone; const num: string);
begin
tel.Numero := num;
WriteLn('NUMERO REAL: ', tel.Numero, ', TIPO: ', tel.Descricao);
end;
var
tel: TTelefone;
begin
tel := TTelefone.Create('41', '65');
try
WriteLn('INTRODUZA O NUMERO DO SEGUINTE FORMATO: COD. OPERADORA + COD. AREA + NUMERO');
WriteLn('=======');
WriteLn;
// inválidos
imprime(tel, '12');
imprime(tel, '+55 41 (99) 999-9999');
WriteLn;
// público
imprime(tel, '190');
WriteLn;
// especial
imprime(tel, '0300 313 4701');
imprime(tel, '0500 313 4701');
imprime(tel, '0800 729 0722');
imprime(tel, '0900 313 4701');
imprime(tel, '3003 3030');
imprime(tel, '4003 3030');
imprime(tel, '4004 3030');
WriteLn;
// fixo
imprime(tel, '3549-5589');
imprime(tel, '(87) 3549-5589');
imprime(tel, '31 (87) 3549-5589');
WriteLn;
// movel
imprime(tel, '9985-0997');
imprime(tel, '(87) 9985-0997');
imprime(tel, '31 (87) 9985-0997');
WriteLn;
// movel SP
imprime(tel, '9 9985-0997');
imprime(tel, '(11) 9 9985-0997');
imprime(tel, '31 (11) 9 9985-0997');
imprime(tel, '031 (11) 9 9985-0997');
imprime(tel, '+55 31 (11) 9 9985-0997');
imprime(tel, '+55 031 (11) 9 9985-0997');
finally
tel.Free;
ReadLn;
end;
end.
This code is working perfectly well in an application in production , I hope it will be useful for other colleagues! =)
I don't know if your doubt is still in your head, but I found a solution.
I found a site, and it contains a list of operators, DDD's and range of prefixes in each state, being it SME and / or SMP. From what I noticed, from time to time they drop an update from this list, but I downloaded the complete ones, both SME and SME, and put them in a table. Follow below the link from where I downloaded these file. http://sistemas.anatel.gov.br/sapn/Default.asp?SISQSmodulo=18096&SISQSsistema=288
After that, I did a simple logic in sql. I think it's easier to show than to explain.
DECLARE
@Telefone VARCHAR(12) = 'ddXXXXXXXX' --<-- COLOQUE O TELEFONE AQUI
,@DDD VARCHAR(2)
,@Prefixo VARCHAR(5)
,@Final INT
SET @DDD = LEFT(@Telefone, 2)
SET @Prefixo = LEFT(RIGHT(@Telefone, 8), 4)
SET @Final = RIGHT(@Telefone, 4)
SELECT
Telefone = CONVERT(VARCHAR, DDD) + CONVERT(VARCHAR, Prefixo) + CONVERT(VARCHAR, @Final)
,Nome
,DDD
,Prefixo
,Final = @Final
FROM Operadora
WHERE DDD = @DDD
AND Prefixo LIKE '%' + @Prefixo
AND @Final BETWEEN Inicial AND Final
I just changed the names of the mailing fields to usable names in tables, but I believe it was quite intuitive.
In this script, if he has any result in the end, it is because it is a mobile and he will put the ninth digit case on the phone he does not Come over. If it does not bring any results in the end, the number is a fixed number.
I saw many answers, but after a few hours analyzing everything we have about Brazilian phones, I created a function to validate the phones, including:
- validation of repeated numbers
- character quantity validation (if it is 10 or 11 numbers, outside the characters that does not count)
- mobile validation (9th digit) if the number has 11 digits
- validation of DDDs ( seed valid DDDs) - thanks @renatoargh
- validate if the number is same phone or radio type (if the number starts between 2 and 5, or 7) - valid only after 2017, if ANATEL does everything right
ANATEL has not yet implemented everything, but when someone sees this and is already in 2017 or later (Look I'm just talking to someone from the future haha) just delete the line that checks the year, which is referenced in the code.
See a working example: JsFiddle
Also follow Gist For those who want to help improve code or report errors: Gist
Thanks also to @ Leandro curious, because I based my code on yours.